Introduction
Deep inside you, on your surface, and all parts in between, fundamental functional units called cells are busy 24/7 keeping your body in a living condition. Curiously, we aren't really in charge of their behavior! In fact, if we were, it is likely we would be in a state of nonliving because of the numerous activities that take place in every cell at all times. Thankfully, we have a nervous system that handles that for us and does not bother us with the trivia of everyday functions. This is an example of the great and miraculous way your body is structurally and functionally composed to address the pressures of the living world.
Plants have cells very similar to yours. So do the other animals. Humans are classified as animals—gasp!—because our cells look and act remarkably like all the other animal cells. Take a look at one of your cells under a microscope, then compare it with a similar one from a duck-billed platypus, if you can find one. If you switched the cells and handed them to a friend, the friend would likely not be able to tell them apart! Try it with a plant cell. But don't bet any money on it this time. The plant cell is likely to have some green things in it that are a sure giveaway. It also has a cell wall, and you don't need one. There are some fundamentals that go into every cell, uniting the world of living things into a oneness of the universe; there are also cellular modifications that make some cells look like they are from a different planet. We can sort it all out in this section. Perhaps you will look at your dog or a plant through new eyes after reading this section.
Cell Theory
While observing dead cork samples with a crude lens, Robert Hooke identified and named “cells.” He thought that the small, simple units looked like the bare prison cells of his time, and the name cell stuck. His work launched a new frontier in scientific exploration that led to modern cell theory:
- All living things are made of cells.
- Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things.
- All cells come from the reproduction of existing cells.
Size Limitations
Bionote
Nerve cells are often long and fibrous-looking. The nerve cell in the leg of a giraffe is often longer than six feet.Most plant cells are approximately 0.002 inches in diameter, whereas most bacteria are even smaller at 0.000008 inches long (10 to 50 nanometers in metric units), making them impossible to see without magnification. Cell size is limited due to the inability of very large cells to provide nutrients and water and remove wastes in an efficient manner. The size limitation is due to the ratio between their outer surface area and the internal volume, making large cubical or spherical cells too big for the surface areas to accommodate all of their cellular life functions. Cells are three-dimensional, so as the cell grows, the volume increases geometrically as the cube of the side length, but actual surface area increases arithmetically with the square of the side length. In other words, a cell's volume increases more rapidly than the surface area. This becomes biologically important when a cell becomes too large for the available surface area to allow passage of nutrients and oxygen into, and cellular waste out of, the cell. Conversely, smaller cells can move materials in and out through the cell membrane at a faster rate because they have a more favorable surface area-to-volume ratio. Interestingly, the shape of muscle and nerve cells tend to be long and thin, which also provides a favorable surface area-to-volume ratio.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Two structurally distinct types of cells have evolved that vary greatly in their internal complexity. Prokaryote cells are the simplest type and are evolutionary precursors to eukaryote cell types. What is thought to be the earliest known fossilized cells were discovered by paleontologists working near the Great Lakes in North America. They discovered microfossil evidence with enough detail to classify the cells as prokaryote. How did they know they were prokaryote?
Although both prokaryote and eukaryote cells can have a cell wall and a cell membrane to enclose the cellular cytoplasm, the structural similarities end there. Inside a typical prokaryote cell, such as a bacteria cell, there are no membrane-bound organelles. An organelle is a subcellular structure that has a specific function. Even the genetic material, although often contained and cornered inside the cell, is not bound by a membrane. Eukaryotic cells, which basically include every cell type except bacteria, are characterized by internal organelles surrounded by a membrane, which helps to increase their organization and efficiency. In contrast to prokaryotes, in eukaryotes the chromosomes are made of distinct lengths of DNA and are stored within a nuclear membrane. Because prokaryotes are simpler, lacking membrane-bound organelles, they are also much smaller (1 to 10 micrometers) than eukaryotes, which range from 10 to 100 micrometers in size.
Viruses
Viruses are small nucleic acid units, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protective protein coat, or capsid, making them little more than packaged genes. Some viruses, such as influenza (flu), have a cloaking protein envelope, making it easier to penetrate a host cell. Other viruses such as HIV also have an unusual complement of enzymes that create interesting products. In general, their overall size ranges from 20 nm to 250 nm (one nanometer, nm = 0.00000004 inches), making them much smaller than any single-celled organism and only visible through an electron microscope. Viruses have plagued man for millennia, causing such human maladies as chickenpox, warts, hepatitis, smallpox, polio, mononucleosis, colds, herpes, and rabies, just to mention a few. Although viruses contain either DNA or RNA, they are actually considered nonliving because they do not grow, reproduce on their own, maintain homeostasis, nor metabolize. Their “life cycle” is an interesting study of deception, pillage, and piracy.
Bioterms
A bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacteria. They are useful because they are easy to study and have added greatly to our knowledge of viruses and how they work.A virus, also known as a phage, can only survive by infecting a living host cell and turning that cell into a factory to manufacture more viruses. Research in molecular biology often studies bacteriophages because they are common and easier to culture and maintain than more pathogenic types. There are two known methods which explain how viruses are spread: lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
Lytic Cycle
In the lytic cycle, the phage always destroys the host cell as the final act of the following five-part event:
- The phage attaches to the cell membrane and injects viral DNA or RNA into the living host cell.
- Injected phage nucleic acids contort into a circle inside the cell.
- The infected cell mistakenly copies the phage DNA or RNA (whichever nucleic acid the phage possesses).
- The copied nucleic acids organize as phages.
- When the number of completely assembled phages becomes too large for the host cell to contain, the cell membrane breaks, releasing numerous phages to infect neighboring cells.
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle also has five stages, but the host cell is not destroyed, but is used to continually reproduce more phages:
- The phage attaches to the cell membrane of a living cell and inserts its DNA or RNA.
- Phage DNA or RNA reforms as a circle inside the host cell.
- Phage DNA becomes incorporated into the host cell DNA, called a prophage.
- Host cell reproduces normally and mistakenly makes new phage nucleic acids at the same time as normal nucleic acids. The phages are released into the environment to infect other cells.
- Under certain conditions, a prophage may switch to a lytic pathway. Otherwise the host cell continues to generate more phages.
Certain viruses have a cloaking cover made of a protein-lipid combination with glycoprotein projections from the surface. These viruses, such as mumps, use their glycoprotein spikes to simulate a normal protein and thereby mask their identity so they can attach to receptor sites on the cell membrane of the host. The envelope then fuses with the cell membrane and allows the viral nucleic acids to spill into the host. Vaccines have been developed and are effective in combating certain viral diseases such as smallpox, mumps, and polio. A vaccine is a harmless variation of the microbe that is designed to stimulate the immune system of the individual.
Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure and Function
Membranes have many different functions within a typical cell, such as keeping unwanted viruses out, but probably the most valuable is the partitioning of the cell into functional and segregated compartments. Because of the incredible number and often conflicting biochemical reactions occurring in a cell at any one time, the cell must retain order via structural organization or risk chemical chaos. The internal membranes compartmentalize reactions to prevent interference. The cell membrane also separates life from the nonlife on its exterior. In so doing, an intact and healthy membrane is selectively permeable because it allows substances needed for cell prosperity to enter and attempts to prohibit the penetration of unwanted and unfriendly substances. Unfortunately the system is not always fool-proof. Sometimes unwanted substances pass through the membrane and may cause trouble within the cell.
Bioterms
A glycoprotein is a molecule used as an identification or address for proteins seeking a particular site for bonding. There are many different types of glycoproteins because of the vast array of sugars that may combine with the proteins that compose them.Interestingly, when a phospholipid is placed in water, it spontaneously folds upon itself to create a double layer, or bilayer. This bilayer phenomenon is also the foundation for the widely upheld fluid mosaic model of membrane structure. The phospholipid molecule has a water-soluble, polar “head” and two fat-soluble, nonpolar “tails.” The hydrophobic tails always try to avoid water and face the inside of the bilayer, whereas the hydrophilic head faces the exterior and the interior.
Within the phospholipid bilayer are many different types of embedded proteins and cholesterol molecules whose presence spawned the term mosaic. From scanning electron microscope images, it was observed that the embedded molecules can move sideways throughout the membrane, meaning the membrane is not solid, but more like a fluid. The membranes also have glycoproteins attached to their surface, which aid in their location and identification of food, water, waste, and other membrane traffic. Each cell has a particular glycoprotein structure based on its need to attract or repel membrane traffic. Refer to the illustration Typical membrane, and note the arrangement of the phospholipid molecules.
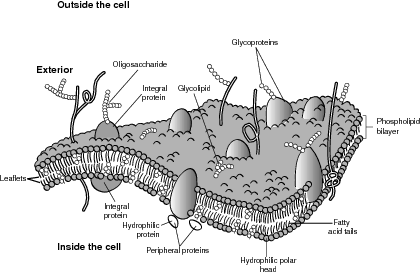
Typical membrane.
The proteins embedded in the membrane serve many of the membrane functions, such as holding the membrane in a regular, identifiable structure for easy bonding. They also have a specific and unique shape that allows them to function as receptors and receptor sites for attachment to the appropriate raw materials needed for cellular functions. In some cases, the receptor protein is also a signal transducer that begins a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions to stimulate a particular reaction or function within a cell. Finally, the transport proteins, also called carrier proteins, help substances move across membranes, as described in the next section.
Passive Transport
Passive transport occurs when no energy is required to move a substance, such as water or carbon dioxide, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal, sometimes across a membrane. The high-to-low concentration gradient is the driving force for passive transport because it fulfills a fundamental law of nature: Things tend to move from a high-energy, ordered structure to a lower-energy, increasing randomness, or increasing entropy state of being. The following are the classes of passive transport:
- Diffusion. This is a good example of how certain molecules, such as oxygen, simply move directly through a membrane in response to the high-to-low concentration gradient. As an example, oxygen diffuses out of the lungs and into the blood for transport to all of the cells.
- Facilitated Diffusion. This is a special type of diffusion that is useful because substances are sometimes too large to move freely through a membrane, or they need to move against a concentration gradient so transport proteins embedded in the membrane assist with the passage. In most cases, the transport protein creates a chemical channel for the passage of a specific substance. Because no energy is expended, the rate of facilitated diffusion depends on the number of transport proteins embedded in the membrane. As an example, glucose is moved by a glucose-transporter protein as it passes through the red blood cell into a body cell.
- Osmosis. This is similar to diffusion except that it refers only to water diffusing through a permeable membrane. Water as a solvent moves from an area of high to low concentration. In biological systems, it is easier to think of water as flowing from a low-solute to a high-solute concentration until the concentration is equal. The solution that has a high-solute concentration is a hypotonic solution relative to another lower-solute concentration or hypertonic solution. Water will continue to osmotically move from the low-solute/high-solvent concentration toward the high-solute/low-solvent concentration until both sides are isotonic, or equal. Osmoregulation is a struggle for all organisms as we continually adjust our cellular water balance for optimal conditions. In your body, the large intestine reabsorbs water by osmosis to help maintain the proper water concentration, which helps to keep your systems from dehydrating.
- Ion channels. These are membrane proteins that allow the passage of ions that would ordinarily be stopped by the lipid bilayer of the membrane. These small passageways are specific for one type of ion, such that a calcium ion could not pass through an iron ion channel. The ion channels also serve as gates because they regulate ion flow in response to two environmental factors: chemical or electrical signals from the cells and membrane movement. This happens in your body when a nervous impulse encounters a gap or synaptic cleft between nerve cells. The electrical stimulation is continued because ion channels are opened to allow specific ions to pass through the receiving membrane, which continues the electrical stimulation to the next nerve cell.
Active Transport
Sometimes substances must be pumped against a concentration gradient, such as the sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+) pump. So a transport protein and energy, usually adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy-rich compound, are needed to push the ions against the gradient. In the case of sodium and potassium ions, maintaining sodium outside and potassium inside the cell is crucial to the functioning of muscles and nerves. The following mechanism illustrates an active transport mechanism:
- Sodium ions inside the cell bind to the transport protein as a phosphate is added from an ATP, which changes the shape of the transport protein.
- The new transport protein structure carries and deposits the sodium to the exterior and bonds with a potassium ion, loses the phosphate group (which again changes the shape of the transport protein), and allows for the return trip.
- The potassium is deposited inside the cell, and a sodium ion and a phosphate are attached to a transport protein to repeat the process.
Endocytosis and exocytosis handle the really big molecules, such as long protein chains or ringed structures, as well as the bulk volume of small molecules. In endocytosis, substances such as food are brought into the cell in a process in which the cell membrane surrounds the particle and moves the particle inside the cell, creating a vacuole or vesicle as a membrane-enclosed container. In exocytosis, waste products or hormones, which are contained in vacuoles or vesicles, exit the cell and their containing membrane is absorbed and added to the cell membrane. There are three types of endocytosis:
- Pinocytosis occurs when the cell absorbs fluid from the exterior, creating a fluid vacuole.
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a special type of pinocytosis that is activated by the identification of a receptor protein sensitive to the specific substance.
- Phagocytosis is the engulfing and digesting of substances, usually food, by vacuoles with a lysosome attached (a lysosome is an organelle that contains digestive enzymes).
Endomembrane System
Unlike a prokaryote cell, all eukaryotic cells, regardless of plant, animal, or other origins, are structurally similar and contain mostly the same organelles, with certain exceptions noted. Eukaryotes are compartmentalized by inner membranes to increase active surface area, increase the sophistication of subcellular reactions, and thereby increase overall efficiency.
Within the eukaryotic cell, the endomembrane system is a functional association of membrane-bound organelles that are interconnected or closely connected that build, store, and transfer biomolecules. The biologically important endomembrane organelles are discussed in greater detail in the sections that follow. Refer to the illustration A typical cell.
The nucleus is the centerpiece of the cell. It stores the DNA in the form of chromatin, which is DNA plus a protein, and also serves as the site where RNA copies DNA to begin protein synthesis. The proteins are made in the ribosomes, which are in turn made by the nucleolus, which is also a nuclear component. The nucleolus is where the ribosomal RNA is made and assembled with proteins to make tribosomal subunits. A double nuclear membrane encompasses and separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Prokaryotes do not have a well-defined nucleus.
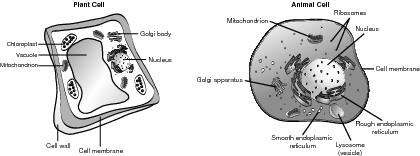
A typical cell.
The rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a long, continuous membrane that has many functions within a cell. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) is prominent in cells that create and export proteins because it has ribosomes attached to the membrane. The rER has two important functions, including making more membrane to lengthen the ER and further compartmentalize the cell. Another function is to make secretory proteins, such as antibodies, that are created to function outside of the mother cell. Secretory proteins and other extracellular exports are enveloped by a transport vesicle and are therefore able to move undisturbed through the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus.
The rER also connects the nuclear membrane to the smooth ER (sER). The sER builds lipids, regulates the calcium levels so muscles perform correctly, and helps break down toxic substances in the liver. They do not contain ribosomes.
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, is not connected to the ER, but receives proteins from the ER and modifies them for extracellular export. When a Golgi apparatus receives a transport vesicle from the ER, it sorts the product into like storage areas, chemically marks them for destination points, repackages them in a new transport vesicle, and releases the resulting package to the cell membrane for extracellular export.
The structure of the Golgi apparatus supports its function. Electron microscopy indicates that the structure resembles interconnected, deflated balls or bags. One end serves as a “receiving point,” the other a “shipping center,” and the middle contains molecules that sort products and synthesize vesicles to surround them.
Lysosomes are sometimes called the cell's suicide pill because they are single-membrane organelles that contain hydrolytic, digestive enzymes that could easily destroy the cell. Their construction begins in the rER where the enzymes and membranes are joined, and finish in the Golgi apparatus. When fully functional, lysosomes are released and operate mostly in animal cells to perform their four primary functions:
- Subcellular digestion of food particles and nonfunctioning organelles
- Recovery and recycling of certain biomolecules for later use by the cell
- Destruction of harmful foreign particles, such as invading bacteria
- Digestion and removal of the webbing between embryonic fingers
Vacuoles, such as lysosomes, are single-membrane-bound sacs filled with fluid. They also serve four major functions, as explained by their use in the central vacuole found only in plant cells:
- Absorb and store water
- Store enzymes until needed, and metabolic wastes until removed
- Contain attractive pigments to lure pollinators to flowers
- Store toxic chemicals, which also serve as deterrents to herbivores
Energy Production: Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
All green plants have chloroplasts that serve as the location for photosynthesis. Although chloroplasts may be found in all above-ground parts of the plant, most are concentrated in the middle, or mesophyll, of the leaf. Chloroplasts are enclosed in a double membrane that creates a fluid-filled compartment between the membranes, called a stroma. Within the stroma are thylakoids, which are stacked like chips into grana. Within the thylakoid membrane are various types of chlorophyll molecules that capture and convert the energy of light into the chemical energy of chemical bonds. The thylakoid membrane greatly increases the available surface area and houses most of the enzymes and machinery for use in photosynthesis. Each photosynthetic cell contains many chloroplasts, which contain many grana.
Like all subcellular organelles, the function of the mitochondria is related to its structure. The primary purpose of the mitochondria is to conduct cellular respiration, converting the chemical energy of food molecules, such as carbohydrates, into high-energy compounds, such as ATP. Similar to chloroplasts, mitochondria are enclosed by a double membrane that creates a fluid-filled intermembrane space. The second compartment, the mitochondrial matrix, is contained by the highly folded inner membrane. The cristae, or folds of the inner membrane, greatly increase the surface area and contain a multitude of enzymes, so most cellular respiration reactions that produce ATP are completed in the mitochondrial matrix.
Endosymbiosis
An American researcher, Lynn Margulis, proposed in 1966 the hypothesis of endosymbiosis, which may explain the advent of the first eukaryote. According to Margulis, there were two successful invasions of an early anaerobic (one not requiring oxygen) prokaryote, by smaller independent prokaryotes. One of these prokaryote invaders entered the larger prokaryote probably for protection and easy access to nutrients, decided to stay, and began to reproduce independently inside the host cell. Rather than try to evict the invader, the two cells developed a mutually beneficial relationship. The invading cell is thought to be the modern-day mitochondria. A second invasion of similar style, but this time by a photosynthetic bacterium, eventually became a chloroplast. Interesting evidence supports this hypothesis. First, both mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA, which is separate and different from the rest of the cell. Second, the arrangement of their DNA is circular, a characteristic of prokaryote cells. Finally, both reproduce independently of the rest of the cell.
Cell Cycle: Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis
Each eukaryotic cell has a repeating set of events that make up the life of every cell, called the cell cycle. Although they vary in length depending upon the cell's function, the cell cycle for all cells can be described in five steps. The first three steps where the cell grows, matures, and carries out its life function are collectively called interphase, followed by mitosis, and cytokinesis. Refer to the illustration Cell cycle.
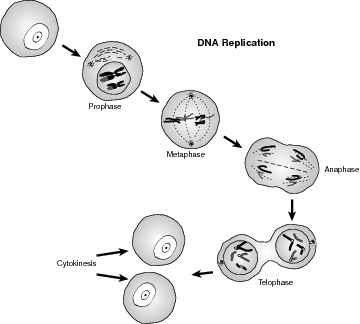
Cell cycle.
Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis
The interphase continuum of stages, G1, S, and G2, begins the process in which the cell grows and matures (G1), followed by the S phase in which the DNA is copied. Finally, the G2 phase is when the cell prepares for division. Mitosis occurs when the nucleus of the cell divides into two identical nuclei with the same number and type of chromosomes, followed by cytokinesis when the cytoplasm, for both plant and animal cells, divides, thus creating two daughter cells that are genetically equal and approximately identical in size.
Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer
Cells regulate their cell cycle in two distinct ways:
- During G1, when the conditions are favorable, certain proteins stimulate the cell to begin copying the DNA (S phase). Likewise, if the cell is not healthy or large enough, or the environmental conditions are not favorable, the cell cycle stops here to prevent cell injury.
Biohazard
Although mutations occur spontaneously in nature, environmental factors may increase their incidence, such as the use of tobacco products, overexposure to ultraviolet light and other type of radiation, and certain viruses.- The cell cycle can also cease during the G2 phase at the DNA replication site. If the DNA is determined to be without blemish, the process continues, if damaged, the cell cycle is suspended until the DNA can be repaired.
If a mutation occurs in one of the genes that controls or regulates cell growth in any number of ways, the corresponding protein may not function correctly, allowing the cell cycle to proceed without interruption. Cancer is a cell-division disorder that results in uncontrolled cell growth.
Asexual Reproduction
When an organism reproduces offspring without the union of gametes, then asexual reproduction has occurred. Gametes are sex cells that are either sperm (male) or egg (female).
Asexual reproduction guarantees that the offspring will be both genetically and structurally identical to each other and their parent. It also allows one parent to rapidly produce offspring, which can be an ecological advantage when exploiting a new ter-ritory. For instance, the foxtail plant is considered a “weed” in certain parts of the Midwest. It is an annual plant that is able to produce enough seeds to cover an exposed area in one growing season. In one sense this is good, because it may prevent erosion; unfortunately, the area covered by the foxtail may be a farmer's field.
It also increases the likelihood that the species will survive, simply because of massive numbers. The identical nature of the offspring is also a potential drawback because of a major change in the environment, or the blanket use of a biocide, or a hungry predator.
Asexual reproduction produces offspring in four distinct methods:
- Budding is when offspring begin as outgrowths or “buds” of the parent. When mature, they drop off and grow into a mature adult. Budding is common in Porifera, like sponges.
- Fragmentation is common in cnidarians and some worms, and occurs when a piece or pieces of an organism are cut off or broken off from the main body. The fragmented piece then grows into an adult.
- Binary fission is a combination of mitosis and cytokinesis because an organism simply divides into two organisms, especially common in flatworms.
- Parthenogenesis is the deposition of unfertilized eggs, often by insects, which grow into adults.
In every case, the offspring are identical to the parent and to each other.
No comments:
Post a Comment